Electronics are related products based on electric energy, including: watches, smart phones, telephones, televisions, DVD players (VCD, SVCD, DVD), video recorders, camcorders, radios, tape recorders, combination speakers, laser players (CD), computers, game consoles, mobile communication products, etc.
Safety testing is essential to ensure safe operating standards for any electrical product. Various governments and agencies have developed stringent requirements for electrical products that are sold world-wide. In most markets it is mandatory for a product to conform to safety standards promulgated by safety and standard agencies such as UL, CE, VDE, CSA, BSI, CCC and so on.
Temperature Humidity Test
Test Standard: IEC62660-2, IEC 60068-2-2
SPS usage
Let’s first explain the electrical appliances we use every day. Wake up early in the morning and turn on the electronic fluorescent lamp. When brushing your teeth, the charger of the rechargeable electric toothbrush, use the remote control to turn on the TV to watch the news, use the induction cooker or microwave to heat breakfast, and go out to take the elevator. When you walk into the office, look around at every kind of machine, telephone, and fax that needed to be plugged in. Basically, the products that need to be used are the possible uses of SMPS. The required specifications and circuit structure vary depending on the place of use, and the price will vary greatly.
Commercial use 0~70 °C
Industrial use -25~125 °C
Military use -40~125 °C
Commercial use 0~40 °C General electrical appliances in daily life, such as users of computers and photocopiers
Industrial -20~71 °C Power used by industrial products, such as power in SMD machines and CNC machines
Military use -40~125 °C Military use, such as power used in missiles, battleships, and tanks.
Test Standard: UL 1642
Temperature cycling test
a) Raising the chamber-temperature to 70±3 ℃(158±5℉)within 30min and maintaining this temperature for 4h.
b) reducing the chamber temperature to 20±3 ℃(68±5℉)within 30 min and maintaining this temperature for 2h.
c) Reducing the chamber temperature to minus 40±3 ℃(- 40±5℉)within 30 min and maintaining this temperature for 4h.
d) Raising the chamber temperature to 20±3 ℃(68±5℉)within 30min.
e) Repeating the sequence for a further 9 cycles.
f) After the 10th cycle, storing the batteries for a minimum of 24h, at a temperature of 20±5 ℃(68±9℉)prior to examination.
Test Standard: IEC 62133
Test Standard: IEC 61960
Test Discharge performance at 20 ℃
This test verifies the rated capacity of a cell or battery.
Step 1-The cell or battery shall be charged.
Step 2-The cell or battery shall be stored, in an ambient temperature of 20±5℃, if not less than 1h and not more than 4h.
Step 3-The cell or battery shall be discharged, in an ambient temperature of 20±5℃,at a constant current of 0,2 lt A, until its voltage is equal to the specified end-of-discharge voltage.
Step 4-The capacity delivered during step 3 shall be not less than 100% of the rated capacity declared by the manufacturer.
Step 1 to 4 may be repeated up to four additional times, as necessary to satisfy this requirement.
Test Discharge performance at -20 ℃
This test determines the capacity of the cell or battery at a low temperature.
Step 1-The cell or battery shall be charged.
Step 2-The cell or battery shall be stored, in an ambient temperature of -20±2℃, for not less than 16h and not more than 4h.
Step 3-The cell or battery shall be discharged, in an ambient temperature of -20±2℃, at a constant current of 0,2 lt A, until its voltage is equal to the specified end-of-discharge voltage.
Test High rate discharge performance at 20 ℃
This test determines the capacity of the cell or battery when discharge at a high rate. This test is not required if the cell or battery is not designed to be used at this rate.
Step 1-The cell or battery shall be charged.
Step 2-The cell or battery shall be stored, in an ambient temperature of 20±5℃, for not less than 1h and not more than 4h.
Step 3-The cell or battery shall be discharged, in an ambient temperature of 20±5℃, at a constant current of 1,0 lt A, until its voltage is equal to the specified end-of-discharge voltage.
Test Standard: IEC 62660-2
Thermal test
This test is performed to characterize cell responses to high-temperature environment.
a) Adjust the SOC of the cell to 100% for BEV application, and to 80% for HEV application.
b) The cell, stabilized at room temperature, shall be placed in a gravity or circulating air-convection oven. The oven temperature shall be raised at a rate of 5K/min to a temperature of 130 ℃. The cell shall remain at this temperature for 30 min before the test is discontinued. If necessary, to prevent deformation, the cell may be maintained during the test in a manner that does not violate the test purpose.
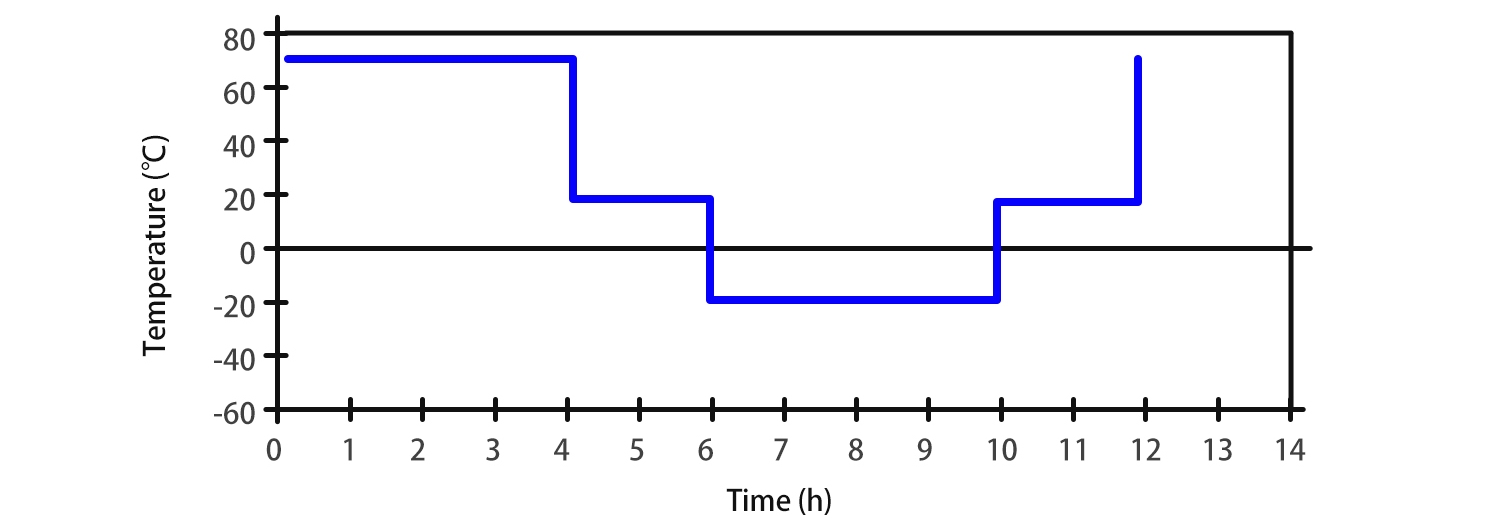
Temperature cycling
This test is performed to characterize thermal durability of a cell by exposing at a low and high temperature environment alternately to cause expansion and contraction of cell components.
a) Adjust the SOC of the cell to 100% for BEV application, and to 80% for HEV application.
b) Perform the temperature cycling in accordance with ISO 16750-4 as shown The minimum operating temperature shall be -40℃ or Tmin specified by the cell manufacturer and the maximum operating temperature shall be 85 ℃ or Tmax specified by the cell manufacturer. Perform 30 test cycles as specified.
Salt Spray Test
Test purposes
It is used to assess the anti-corrosion ability of materials and their protective layers, as well as the process quality comparison of similar protective layers. It can also be used to assess the salt spray corrosion resistance of certain products.
Test conditions
The salt solution is prepared with sodium chloride and distilled water, and its concentration is 5±0.1% (weight). The collected liquid after physicalization shall not be reused except for the back part of the baffle.
The pH value of the salt solution before atomization is between 6.5 and 7.2 (35 ℃). When configuring the solution, it is allowed to use chemically pure or above dilute hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to adjust the pH value, but the concentration must still be in line with the 80cm2 funnel to collect the salt spray precipitation for 16 hours of continuous atomization, any position in the effective space The sedimentation rate is: 1.0~2.0ml/h.80cm2.
This standard uses continuous atomization, and the recommended standard time is 16, 24, 48, 96, 168, 336, 672h.
The atomization must prevent oil pollution, dust impurity and the temperature and humidity of the sprayed air.
Test Standard: IEC 60068-2-11
Salt solution
Concentration: The salt used in the test should be high-quality sodium chloride. When dried, the content of sodium iodide should not exceed 0.1%, and the total content of impurities should not exceed 0.3%.
The concentration of the salt solution should be (5±1) % (mass ratio)
The solution should be prepared by the following method, the mass of (5 ± 1) parts of salt solution in 95 parts of distilled water or deionized water.
PH value: When the temperature is (35±2)℃, the pH value of the solution should be within 6.5~7.2.
During the condition test, the pH value should be maintained within this range. Under the premise of ensuring the concentration of sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid or sodium chloride can be used.
Adjust pH value: pH value should be measured for every new batch of solution.
Air supply
The compressed air entering the spray device should be free of impurities such as oil and dust.
Measures should be taken to make the humidity and temperature of the compressed air meet the requirements of the operating conditions. The air pressure should be properly generated from a small, humid, dense mist.
In order to prevent salt deposits from clogging the spray device, it is recommended that the relative humidity of the air at the nozzle be at least 85%. One possible method is as follows: let the air flow through the automatically maintained hot water tower in the form of very small bubbles, with a water temperature of at least 35°C.
The allowable water temperature increases with the increase of air flow and the decrease of the insulation of the test chamber and the environment.
The water temperature should not be too high, so as not to bring too much water into the test chamber, nor exceed the specified operating temperature.
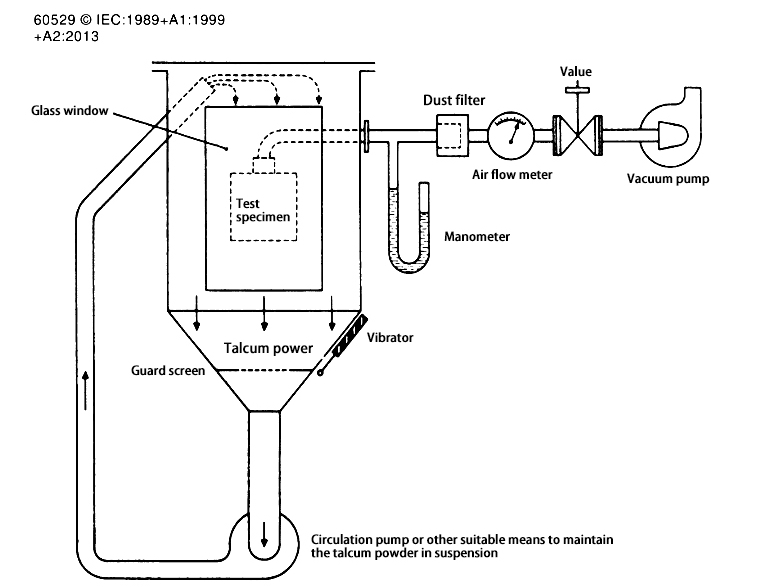
Sand and Dust Test
Test Standard: IEC 60529
Water Spray Test
Test Standard: IEC 60529; ISO 20653
Table 3 - Degree of protection against water indicated by the second characteristic number
Second characteristic number | Degree of protection | |
Brief description | Definition | |
0 | Non-protected | - |
1 | Protected against vertically falling water drops | Vertically falling drops shall have no harmful effects. |
2 | Protected against vertically falling water drops when enclosure tilted up to 15° | Vertically falling drops shall have no harmful effects when enclosure is tilted at any angle up to 15°on either side of vertical. |
3 | Protected against spraying water | Water spray at an angle up to 60°on either side of the vertically shall have no harmful effects. |
4 | Protected against splashing water | Water splashed against the enclosure from any direction shall have no harmful effects. |
5 | Protected against water jets | Water protected in jets against the enclosure from any direction shall have no harmful effects. |
6 | Protected against powerful water jets | Water protected in powerful jets against the enclosure from any direction shall have no harmful effects. |
7 | Protected against the effects of temporary immersion in water | Ingress of water in quantities causing harmful effects shall not be possible when the enclosure is temporarily immersed in water under standardized conditions of pressure and time. |
8 | Protected against the effects of continuous immersion in water | Ingress of water in quantities causing harmful effects shall not be possible when the enclosure is continuously immersed in water under conditions which shall be agreed between manufacturer and user but which are more severe than for numeral 7. |
9 | Protected against high temperature and pressure water jets | Water protected at high pressure and temperature against the enclosure from any direction shall have no harmful effects. |
Mix Gas Corrosion Test
Test Standard: EIA-364-65
Coupon evaluation equipment
Weight gain equipment such as analytical balance or equivalent with an accuracy of one microgram or better, see ASTM B-810, Calibration of Atmospheric Corrosion Tests by Mass Change in the Mass of Copper Coupons.
The environmental chamber shall consist of an enclosure made of nonreactive (will not react with pollutant gases) materials contained within a cabinet, oven, or incubator capable of maintaining the temperature within the specified ranges: see table1. A commercially available environmental chamber will suffice as the outer chamber, if applicable.
Table 1 Environmental classes
Class | Relative Humidity, % | Temperature, ℃ | Concentration, ppb | |||
Cl2 | NO2 | H2S | SO2 | |||
I | Discontinued as a test procedure | |||||
II | Superseded by class IIA | |||||
IIA | 70±2 | 30±1 | 10±3 | 200±50 | 10±5 | 100±20 |
III | Superseded by class IIIA | |||||
IIIA | 70±2 | 30±1 | 20±5 | 200±50 | 100±20 | 200±50 |
IV | 75±2 | 40±2 | 30±5 | 200±50 | 200±20 | N/A |
Test Standard: IEC60068-2-60
Table 1 Test method and parameters
Test parameters | Method 1 | Method 2 | Method 3 | Method 4 |
H2S(10-9vol/vol)a | 100±20 | 10±5 | 100±20 | 10±5 |
NO2(10-9vol/vol)b | -- | 200±50 | 200±50 | 200±20 |
Cl2(10-9vol/vol)c | - | 10±5 | 20±5 | 10±5 |
SO2(10-9vol/vol)d | 500±100 | - | - | 200±20 |
Temperature(℃) | 25±1 | 30±1 | 30±1 | 25±1 |
Relative humidity(%) | 75±3 | 70±3 | 75±3 | 75±3 |
Number of volume changes per hour of test gas(10) | 3~10 | 3~10 | 3~10 | 3~10 |
Weight gain of copper sheet sample obtained according to Appendix A(mg/(dm2·d)) | 1.0~2.0 | 0.3~1.0 | 1.2~2.2 | 1.2~2.4 |
Note: Due to the different corrosivity of test methods 1 to 4, the order of numbering and the corresponding corrosion weight of copper pieces do not reflect its severity level | ||||
a H2S: 1μm/m3=0.71mm3/m3 b NO2: 1μm/m3=0.53mm3/m3(10-9vol/vol)b=UNIT(μm/m3) c Cl2: 1μm/m3=0.34mm3/m3 d SO2: 1μm/m3=0.38mm3/m3 | ||||